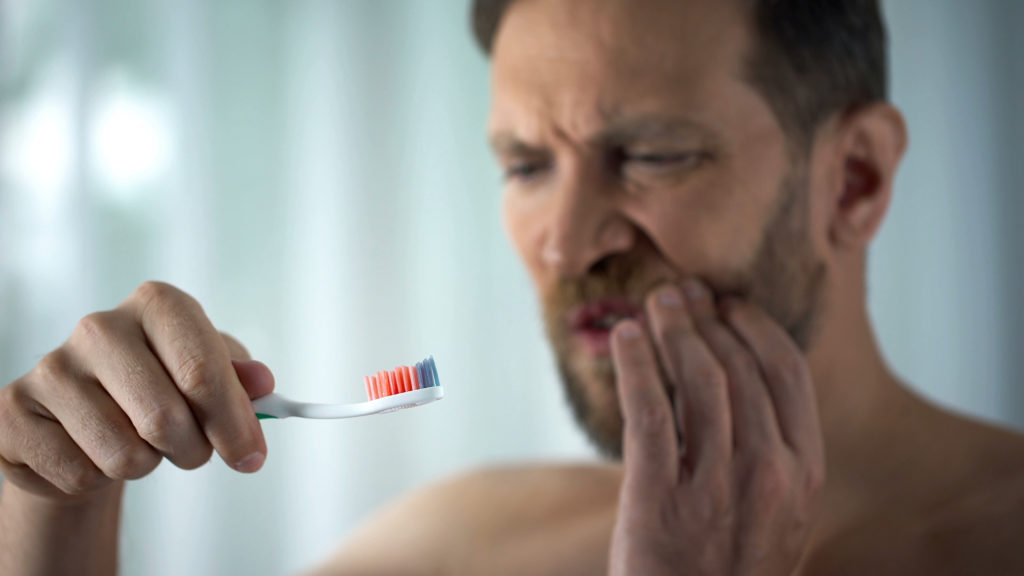
Think bleeding gums are harmless? Although it may seem very common, it's a phenomenon that needs to be taken seriously. Many Swiss people find that their gums bleed after biting into a hard food or forcing themselves to brush their teeth. Whether it's a one-off bleed, gingivitis or a sign of a more serious pathology, find out more about the common causes of gum bleeding and the reflexes to adopt to prevent the situation from getting worse.
Types of gum bleeding
Healthy gums are pink and do not bleed. Patients who consult a dentist in Lausanne or a dental center in Fribourg may experience a variety of gingival bleeding. There are two main categories:
Acute gingival bleeding:
Gums bleed occasionally and temporarily. This may be due to eating food that is hot, difficult to chew or contains sharp pieces. Aggressive brushing or the use of a hard toothbrush can also irritate gums to the point of bleeding. In this case, we speak of a mechanical gum problem. This phenomenon is not indicative of an ailment, and disappears rapidly within a few days.
Recurrent or chronic gingival bleeding:
If gums bleed regularly, it's usually gingivitis, or inflammation of the gums. This most often occurs when plaque is not effectively removed by brushing. As a result, the tissues supporting the teeth are weakened, and the slightest contact leads to bleeding. Untreated gingivitis eventually leads to periodontitis and tooth loosening.
Why do gums bleed?
Apart from mechanical irritation (aggressive brushing and consumption of certain foods), gingival bleeding is sometimes linked to oral diseases. Only a dental surgeon can diagnose and treat them.
1 - Gingivitis
Are your gums red, swollen, painful and bleeding? These are the symptoms of gingivitis, the leading cause of bleeding gums in Switzerland. Some patients are at greater risk of developing gingivitis. These include pregnant women, the elderly and people with braces. In addition, malformations or incorrect positioning of the teeth increase inflammation, as it often develops in the interdental space.
2 - Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis develops into periodontitis. This is a more severe form of inflammation that affects the tissues supporting the teeth. You will then be referred to a periodontista speciality of dentistry. HELVIDENT practices in Lausanne, Fribourg and Aigle treat inflammatory diseases of the periodontium.
3 - Mouth ulcer or aphta
This oral disease particularly affects children and women. The bleeding is accompanied by severe discomfort and superficial sores on the oral mucosa. The condition affects around 1 in 5 people at least once in their lives.
Other factors in gingival hemorrhage
Recurrent or chronic gingival bleeding is sometimes a side effect of general pathologies such as :
- Coagulation problems (hemophilia, leukemia)
- Platelet disorders (idiopathic purpura, uraemia)
- Vascular diseases
- Diabetes
- Mercury poisoning
- Cancer
- Hormonal imbalances
Be aware that certain medications (anxiolytics, salicylates, anticoagulants) can cause your gums to bleed. They alter blood pressure, limit the effectiveness of your immune defenses, or dry out your mouth.
Smoking, alcoholism and dietary imbalances are also responsible for some gum bleeding. This is particularly true of vitamin C and K deficiencies. We invite you to discover 9 foods that protect your oral health.
What to do about bleeding gums?
Keep in mind that healthy gums don't bleed. If you notice a change in color, pain or bleeding, something is wrong. So you need to act quickly by making an appointment at a dental practice.
In fact, an oral health professional will be able to diagnose gingivitis or periodontitis that might otherwise have gone unnoticed. As a preventive measure, we recommend consulting a dentist at least once a year for adults, and twice a year for children. He will detect and treat any pathologies in good time. This will help prevent bleeding, a frequent cause of dental emergencies in Lausanne.
Preventive measures for healthy gums
As a general rule, we recommend that you maintain a low good oral hygiene to prevent plaque formation. Brush your teeth and gums at least twice a day (after meals) with a fluoride toothpaste. Brush from gum to tooth, at a 45° angle. Ask your dentist for regular scaling.
Don't hesitate to ask the advice of a dental hygienist in Lausanne to improve your gestures. This professional can also advise you on the use of dental floss, an interdental brush or an electric toothbrush. By adopting the right accessories and the right reflexes, you can eliminate as many food residues and bacteria as possible from your mouth.
HELVIDENT welcomes you to one of its three dental clinics in Fribourg, Lausanne or Aigle. Our complete team is at your disposal for a preventive or curative consultation. Contact us for an appointment.